JKB-122
JKB-122 is currently under development as a small molecule and a long-acting TLR4 antagonist targeting AIH / NASH / CLD
| Discovery | Lead | Pre-Clinical | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | NDA |
JKB-122 Overview
JKB-122 is a small molecule and a long-acting TLR4 antagonist. This drug has demonstrated in preclinical models anti-fibrotic, immuno-modulating, and anti-inflammatory activities and improvement of liver injuries by hepatoprotectant property.
TaiwanJ accomplished the following milestones prior to license:
- AIH (Autoimmune Hepatitis) US patent awarded 2017-0912 (US 9757372)
- NAFLD/NASH US patent awarded 2018-0814 (US 10045977)
- Slow Release Formulation patent is under PCT pathway (WO2019/156904A1)
- Prodrug Formulation patent is under PCT pathway (WO2019/246353A1)
- Obtained AIH (Autoimmune Hepatitis) Orphan Drug Designation from US FDA in 2015-Jan
- Showed positive results in Phase 2 trial on CLD (Chronic Liver Disease) (unblinded on 2017-0830)
- Showed positive results in Phase 2 trial on NAFLD (unblinded on 2018-1011)
- Showed positive results in Phase 2 trial (open label) on AIH (announced on 2019-0121)
JKB-122 NASH
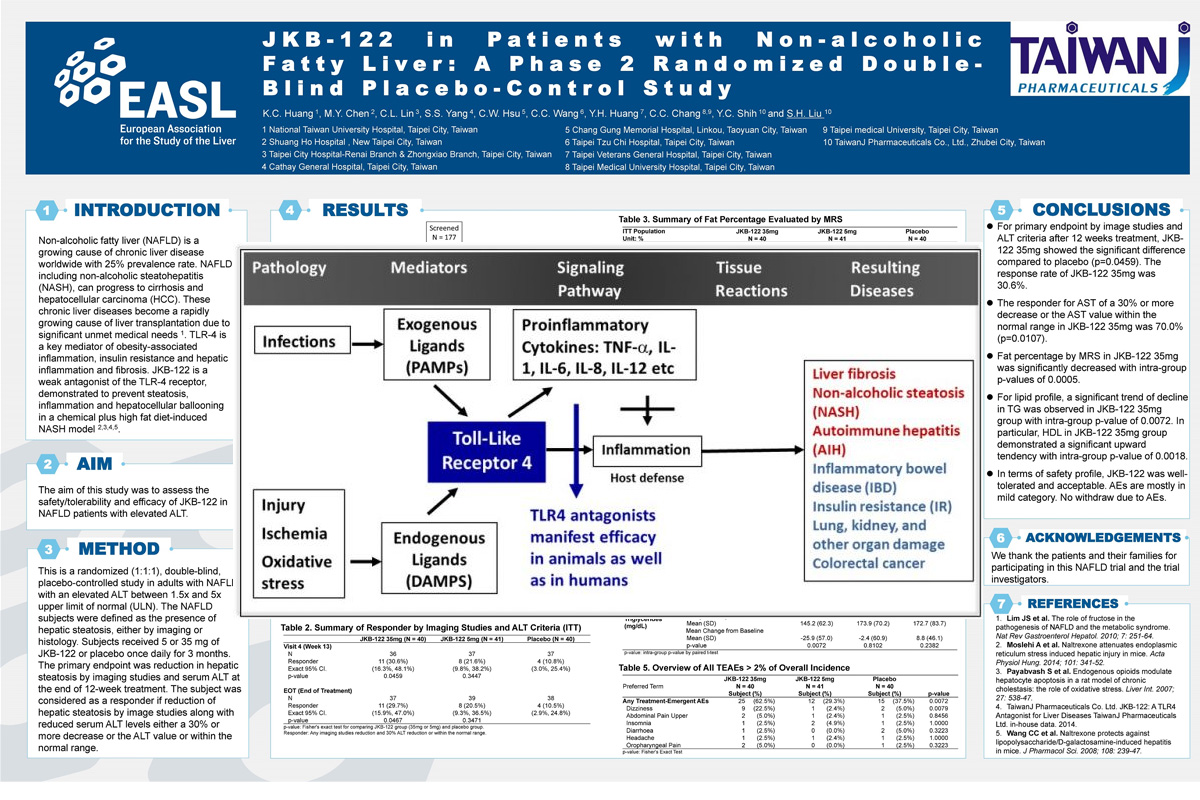
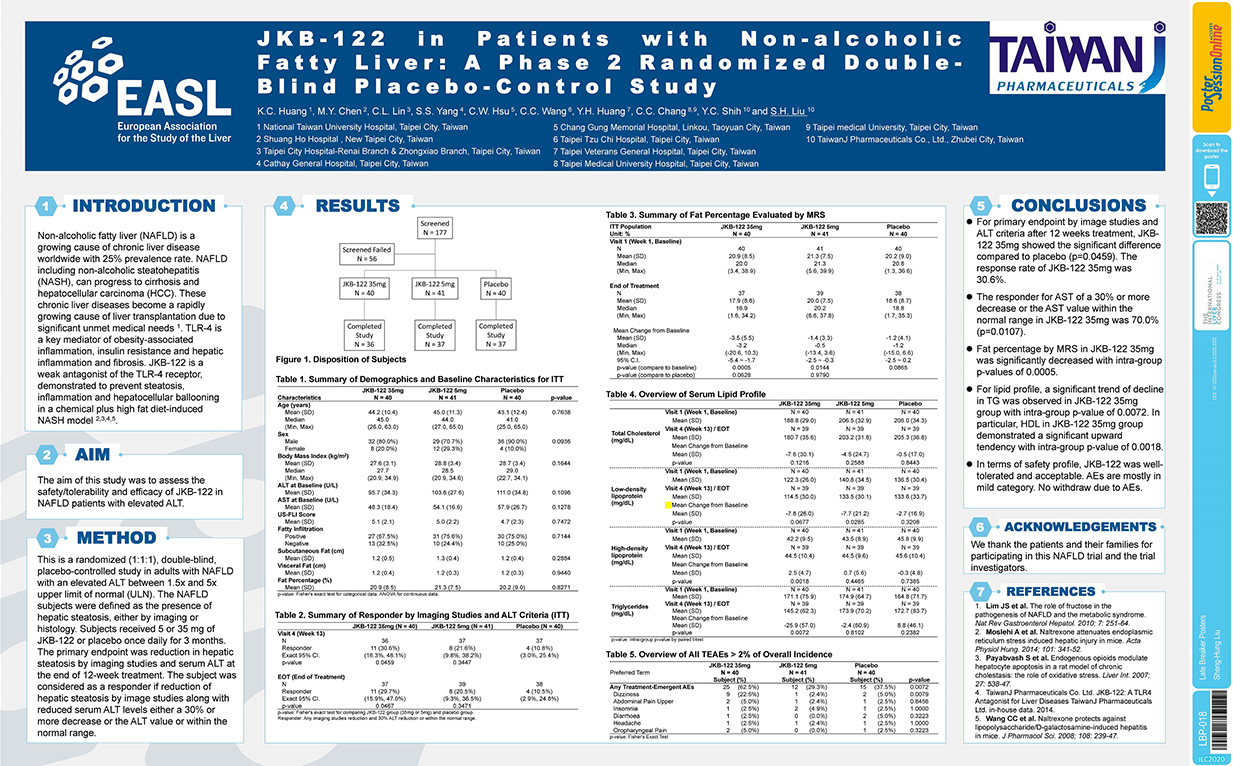
Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD) is a growing cause of chronic liver disease worldwide with 25% prevalence rate. NAFLD including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These chronic liver diseases become a rapidly growing cause of liver transplantation due to significant unmet medical needs. TLR-4 is a key mediator of obesity-associated inflammation, insulin resistance and hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. JKB-122 is a weak agonist of the TLR-4 receptor, demonstrated to prevent steatosis, inflammation and hepatocellular ballooning in a chemical plus high fat diet-induced NASH Model
List of Studies
NCT04371718
Effect of JKB-122 on Prednisolone and Azathioprine Induced Remission in Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH)
Conditions: Autoimmune Hepatitis
NCT02556372
Liver Test Study of Using JKB-122 in Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) Patients Who Are Refractory or Intolerant to Current Therapies
Conditions: Autoimmune Hepatitis
NCT02293941
Liver Test Study of Using JKB-122 in Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)-Positive Patients Nonresponsive to Prior Interferon Based Therapies
Conditions: Chronic Hepatitis C
NCT04313205
A Pharmacokinetic Study of JKB-122 Tablets Compared to Capsule
Conditions: Autoimmune Hepatitis
NCT04255069
A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of JKB-122 in Patients With NASH and Fibrosis
Conditions: Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) With Fibrosis

Summary
LBP18
JKB-122 in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a phase 2, randomized, multiple-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
Kuo-Chin Huang1, Ming-Yao Chen2, Chih-Lin Lin3, Sien-Sing Yang4, Chao-Wei Hsu5, Chia-Chi Wang6,7, Yi-Hsiang Huang8,
Chun-Chao Chang9,10, Ying-Chu Shih11, Sheng-Hung Liu11. 1National Taiwan University Hospital, Department of Family Medicine, Taipei, Taiwan; 2Shuang Ho Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, New Taipei, Taiwan; 3Taipei City Hospital-Renai Branch & Zhongxiao Branch, Division of Gastroenterology, Taipei, Taiwan; 4Cathay General Hospital, Liver Center, Taipei, Taiwan; 5Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Taoyuan, Taiwan; 6Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Taipei, Taiwan; 7Tzu Chi University, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation and School of Medicine, Haulien, Taiwan; 8Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Department of Medicine, Taipei, Taiwan; 9Taipei Medical University Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Taipei, Taiwan; 10Taipei Medical University, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei, Taiwan; 11TaiwanJ Pharmaceuticals, Hsinchu County, Taiwan
Email: wallaceliu@taiwanj.com.
Background and aims: Non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD) is a growing cause of chronic liver disease worldwide with 25%prevalence rate. NAFLD including nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. These chronic liver diseases become a rapidly growing cause of liver transplantation. JKB-122 is a weak antagonist of the TLR-4, demon-strated to prevent steatosis, inflammation and hepatocellular ballooning in a NASH mouse model. The aim of this study was to assess the safety/tolerability and efficacy of JKB-122 in NAFLD patients with elevated ALT.
Method: This is a randomized (1:1:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled study in adults with NAFLD with an elevated ALT between 1.5× and 5× upper limit of normal. The NAFLD subjects were defined as the presence of hepatic steatosis, either by imaging or histology. Subjects received 5 or 35 mg of JKB-122 or placebo once daily for 3 months. The primary endpoint was reduction in hepatic steatosis by imaging studies and serum ALT at the end of 12-week treatment. The subject was considered as a responder if reduction of hepatic steatosis by image studies along with reduced serum ALT levels either a 30% or more decrease or the ALT value or within the normal range.
Results: 121 subjects were randomized (Mean age, 44 ± 11 years; man, 80%; mean BMI 28 ± 3.3 Kg/m2; mean liver fat content (LFC) 20.8 ± 8.3%; and mean ALT 103.4 ± 32.7 U/L) and a total of 110 subjects completed all treatment visits and follow-up visit. For primary endpoint by image studies and ALT criteria after 12 weeks treatment, in the per protocol population 11 of 36 subjects, 8 of 37 subjects and 4 of 37 subjects met the definition of a responder in JKB-122 35 mg, 5 mg and placebo arm, respectively. The response rate of JKB-122 35 mg was significantly higher than that of placebo (30.6% vs. 10.8%, p-value = 0.0459). At the end of treatment, mean changes from baseline of fat percentage by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) were −3.5% ± 5.5%, −1.4% ± 3.3%, and −1.2% ± 4.1% in JKB-122 35 mg, 5 mg and placebo arm, respectively. JKB-122 35 mg and 5 mg arms both had a significant difference in mean change from baseline of fat percentage (p-values = 0.0005 and 0.0144). The LFC reduced >10%absolute rate of JKB-122 35 mg was higher than that of placebo (30.0%vs. 3.8%). JKB-122 35 mg also significantly improve BMI, LDL, HDL, total cholesterol or triglycerides compared to placebo. The most frequent AEs in 35 mg JKB-122-treated patients were dizziness (22%vs 5% in placebo), and most treatment emergent AEs were mild to moderate.
Conclusion: JKB-122 35 mg improves NAFLD in primary efficacy endpoint and some secondary efficacy endpoints, such as ALT, liver fat content in MRS image, cCK-18 level and Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score, although no significant inter-group difference was observed compared to placebo. In term of safety profile, JKB-122 was well-tolerated.


